Introduction
In today’s competitive and dynamic business environment, software development is increasingly driven by the focused needs of customers and businesses, both of whom require rapid response to their requirements. Feedback must be immediately incorporated into products and engineering teams must be able to deliver the exact product their customer is looking for on time.
In response, IT teams in multiple industries are now using agile practices to accelerate development and respond to change.
Agile development practices have steadily risen to become a trusted and preferred method of development for software teams in the software industry. Using agile methods, organizations can respond to market changes faster, deliver higher-quality products, and gain a significant competitive edge.
One of the most popular agile methodologies which our company integrates into the development process of its software solutions, and is becoming our company’s policy is “Scrum”.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is one of the most popular Agile methodologies, most often used to manage complex software and product development. It is an adaptive, iterative, incremental, flexible, and effective methodology, designed to focus on delivering the highest business values in the shortest time throughout a project.
Scrum is a framework that helps people address complex adaptive problems, while productively and creatively delivering products of the highest possible value.
The Scrum framework consists of Scrum Teams and their associated roles, events, artifacts, and rules. Each component within the framework serves a specific purpose and is essential to Scrum’s success and usage. Scrum uses fixed-length iterations, called Sprints, which are typically two weeks or 30 days long. Scrum teams attempt to build a potentially shippable (properly tested) product increment with every iteration.
What characterizes this methodology?
This methodology is characterized by the focus that it places on the delivery of business requirements, an agile working environment, collaborative team approach that increases productivity and communication within the team. It always puts an emphasis on cooperation with the client and protects the team from obstructions.
The main characteristics of Scrum:
- Iterative and incremental development process
- Development of software solutions with rapidly changing requirements
- Product progress in a series of “Sprints”
- Requirements are captured as stories in a list of “Product Backlog”
- Uses generative rules to create an agile environment for delivering projects
- Self-organizing and cross-functional teams
- Team-based collaborative approach
- Improves communication and enhances cooperation
- Increases the productivity
- Protects the team from obstructions
- Always focus on the delivery of the highest business values
- No specific engineering practices prescribed
Scrum enables teams to self-organize by encouraging physical co-location or close online collaboration of all team members and daily face-to-face communication among all team members and disciplines in the project. It provides a structure of roles, meetings, rules, and artifacts. Teams are responsible for creating and adapting their processes within this framework.
Why Scrum?
There are a few main points and benefits that separate Scrum from other methodologies:
- The methodology itself has clearly defined rules, roles, and work processes
- Scrum has three main roles: Product Owner, Development Team, and Scrum Master
- The process promotes an agile working environment and transparency
- The projects are divided and realized in iterations called “Sprints”
- We have short iterations in which all the parties are concerned
- The time frame of the sprints can be from 1 to 4 weeks
- Business requirements and tasks are defined in the form of “Stories”
- Each story includes one functionality and is divided into several sub-tasks
- Provide better estimates while spending less time creating them
- It puts an emphasis on communication
- We have a self-organized and cross-functional team
- At the end of every Sprint, there is an assessment of whether the product is acceptable and has met the expectations of the client
- The direction of the project is adjusted on the basis of the work done
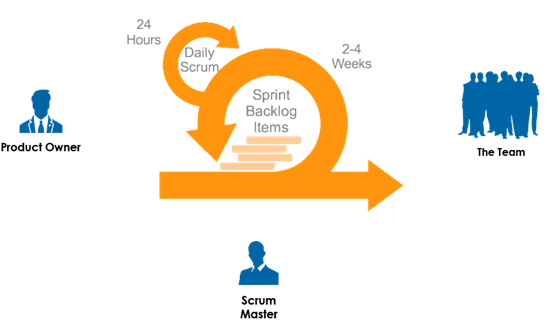
Scrum Process Overview
A Scrum process is distinguished from other agile processes by specific concepts and practices, divided into the three categories of Roles, Artifacts, and Events.
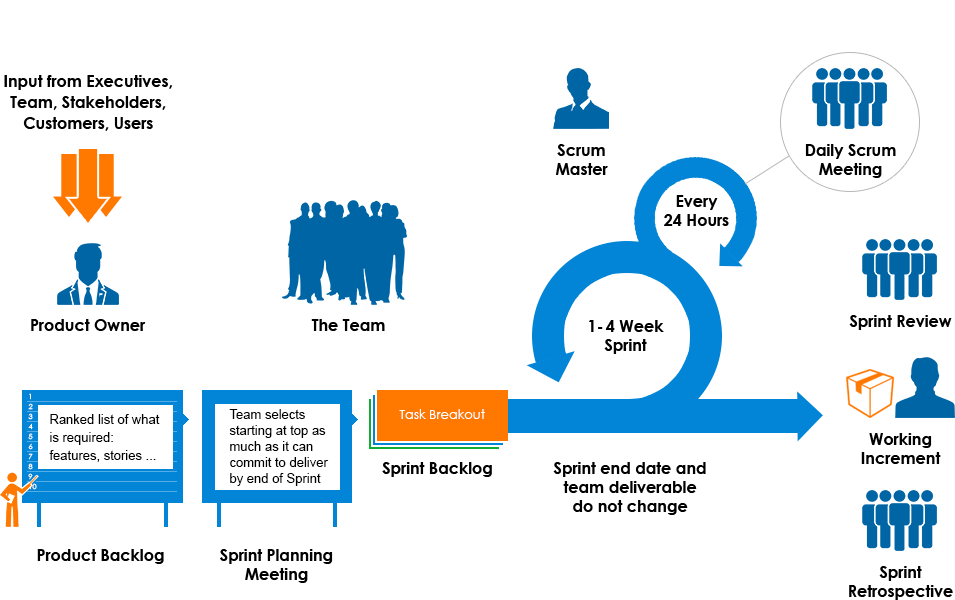
- A “Product Owner” creates a prioritized list called a “Product Backlog”
- During ”Sprint Planning”, the team pulls a small chunk from the top of that list, a sprint backlog, and decides how to implement those pieces
- The team has a certain amount of time – a “Sprint” (usually two to four weeks) to complete its work, but it meets each day to assess its progress (daily Scrum)
- Along the way, the “Scrum Master” keeps the team focused on its goal
- At the end of the Sprint, the work should be potentially shippable, ready to hand to a customer, put on a store shelf, or show to a stakeholder
- The Sprint ends with a “Sprint Review” and “Retrospective”
- As the next Sprint begins, the team chooses another chunk of the Product Backlog and begins working again
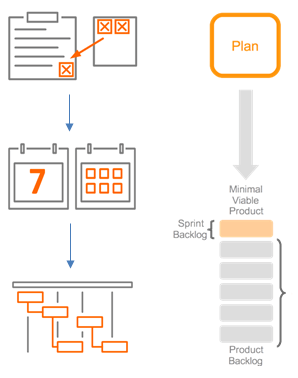
How to apply Scrum in everyday business?
There are several ways how Scrum can be applied in everyday business. Scrum is a dynamic methodology that is adaptable and can be integrated into any software solution regardless of its nature and dynamics.
The main steps for the application of this methodology are:
- It is necessary to define short tasks that are part of the business requirements of the client
- A short-term commitment and cooperation is required of all stakeholders in the process
- A daily summary of the completed work and active problems is needed
- Feedback information is needed from the client for process improvement
Agile vs. traditional Waterfall
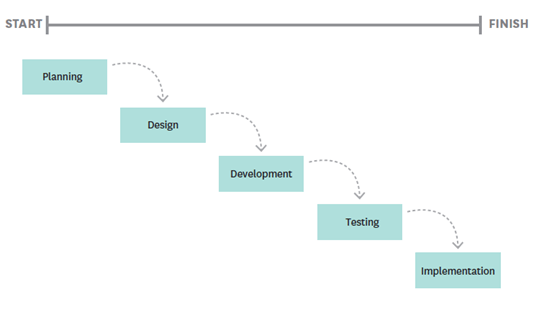
Waterfall SDLC
Sequential development process where all required activities in the preceding phases are complete.
Agile SDLC
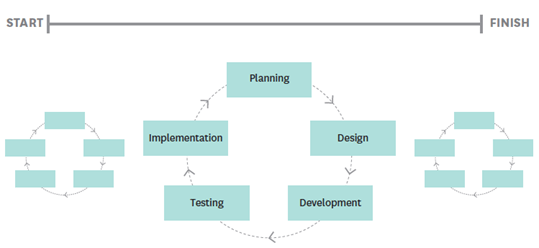
Software development method based on iterative and incremental development encouraging rapid and flexible responses to change Planning Implementation Testing Design Development.
Conclusion
The benefits of Agile software development are real, especially for companies looking to accelerate time to market and move quickly in the software industry.
As part of our software development life cycle, Scrum offers us benefits in several areas. Using this methodology we determined that Scrum increases software quality and team productivity while lowering costs and time. Using this methodology we successfully managed to deliver our solutions in the shortest time with high business value in a transparent environment where all stakeholders in the process are involved, and in each iteration, we produced a working product, which is not the case once compared with traditional Waterfall approach where we have a sequential development process.
Main benefits of Scrum:
- Increase the quality of the deliverables
- Delivers products in a short time period
- It allows the client to change priorities and demands very quickly
- It adds value to the business
- Promotes a better working environment for management
- Promotes transparency and improved client relations
- Enhances the credibility with the client due to the higher product quality
- Creates motivated and inspired team members

