TLS is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication. The 2-way TLS ensures that both parties involved in the communication are identifying each other before a connection is made (regardless if the communication is user-to-user, user-to-machine or machine-to-machine).
In order to demonstrate the two-way TLS authentication between the applications, we are going to make the following:
- Generate a client and server keystores and truststores (using Java Keytool)
- Create simple Mule app
- Configure TLS globally in Mule
Generate client/server keystores and truststores
Client/server keystores and trustores have different contents:
- server’s keystore contains the private and the public key of the server and the truststore contains certificates of the trusted clients
- client’s keystore contains the private and the public key of the client, while the truststore contains certificates of the trusted servers
The keystore contains one or two passwords:
- password for or accessing the keystore file
- keyPassword for accessing the server’s private key in the keystore
1. Generate server keystore
2. Generate client keystore
3.Export the client certificate [client.crt] from the client-keystore.jks
4. Create server truststore and import the client.crt
5. Export the server certificate [server.crt] from the server-keystore.jks
6. Create client truststore and import the server.crt
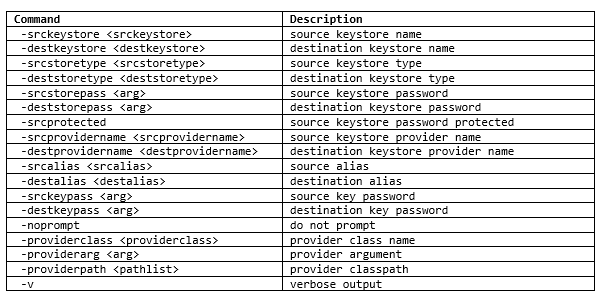
Useful commands:
Create a simple Mule project and configure 2-way TLS
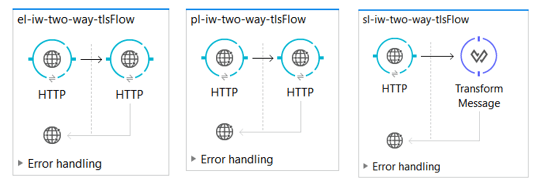
We are going to use 3 simple Mule applications (3 layers). No complex logic there. The first application has an HTTP receiver that runs on port 8092 that is going to receive the GET call. This application will call the pl application. In the end, the pl is going to call the sl application where we are setting some payload:
The next step is to set the configuration for mutual authentication:
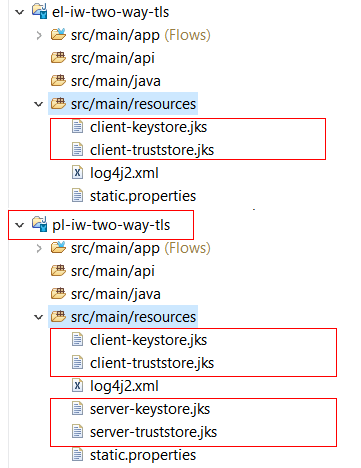
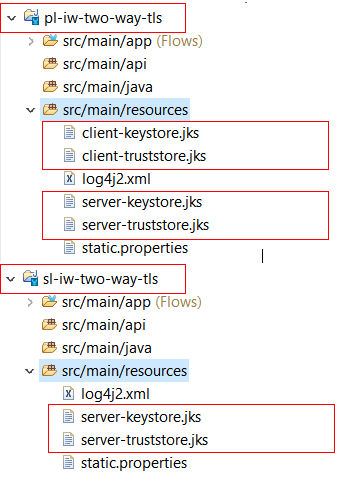
1. Copy the generated keystores/truststores in the projects (under src/main/resources)
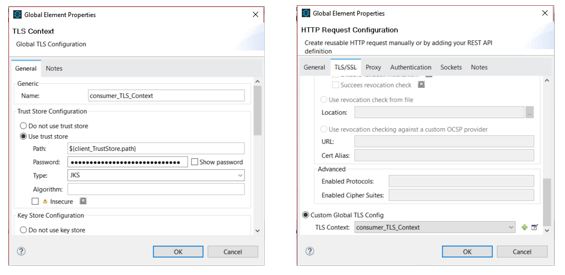
2.Define TLS Context globally and configure the 2-way TLS
- el-iw-two-way-tls
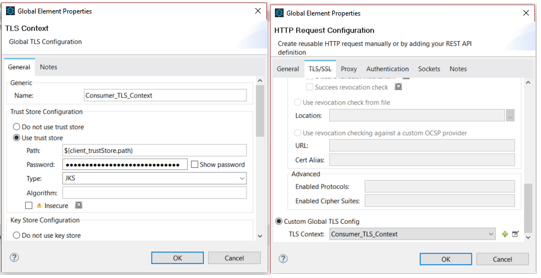
Configure the HTTP Request
- pl-iw-two-way-tls
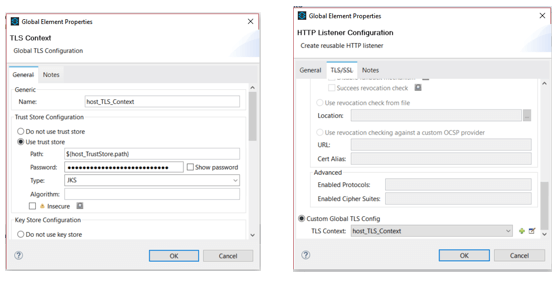
Configure the HTTP listener
Configure the HTTP Request
- sl-iw-two-way-tls
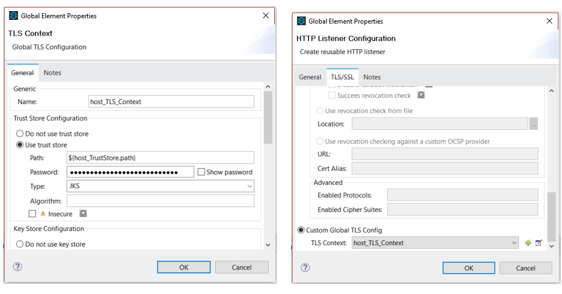
Configure the HTTP Listener
Note: The details of TLS connection negotiations can be seen in the console if we add the below command when we run our applications in debug mode:
-Djavas.net.debug=all or -Djavax.net.debug=ssl:handshake

